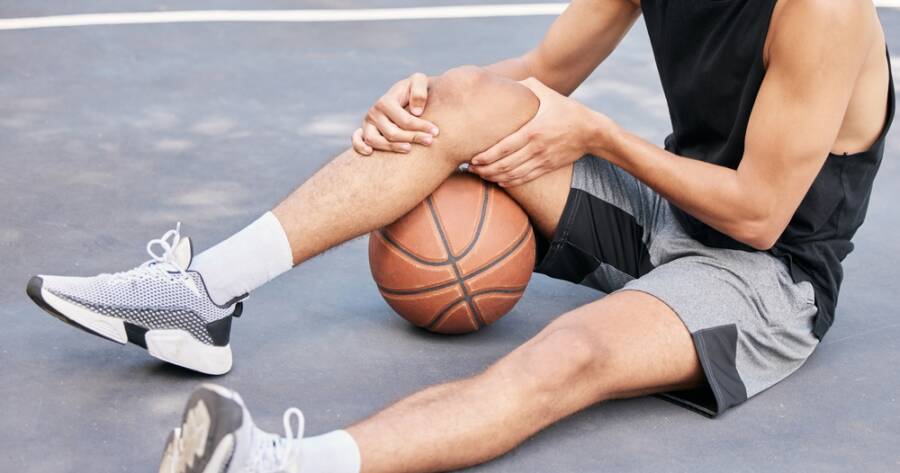
Knee pain can affect anyone, caused by injury, overuse, or health conditions. Recognizing early signs like stiffness, swelling, or sharp pain is key. Proven treatments and long-lasting relief strategies, such as physical therapy, low-impact exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help manage it.
Recognizing Knee Pain Before It Worsens
If you’re beginning to experience discomfort in your knees, recognizing the early signs of knee pain could help you address potential issues before they worsen and become more difficult to treat.
Stiffness in the Knee:
- You may notice stiffness in your knee, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods. This stiffness may seem like a minor inconvenience, but if it continues or worsens over time, it could be an early indication of joint-related conditions like osteoarthritis or tendonitis. Pay attention to whether the stiffness goes away after moving around or persists throughout the day.
Swelling:
- Swelling is often an overlooked symptom, especially when there hasn’t been an obvious injury. If your knee looks or feels swollen, it might be due to internal inflammation. This could be caused by overuse, injury, or even underlying conditions like bursitis or arthritis. Swelling is your body’s way of signaling that something is wrong, so it’s important to not ignore it, even if it seems minor at first.
Knee Giving Way or Locking Up:
- If you experience your knee giving way or locking up while walking, standing, or moving, it could indicate potential ligament or cartilage damage. These symptoms may start off as occasional occurrences, but if left untreated, they could become more frequent or severe. This kind of instability in the knee should be evaluated early to prevent further damage.
Sharp, Localized Pain:
- Sharp pain in specific areas of the knee during activities such as going up or down stairs, squatting, or standing from a seated position can be a sign of something more serious, like a meniscus tear. This type of pain might initially be mistaken for overexertion or muscle strain, but if it persists, it’s important to take it seriously. Chronic pain during these movements often points to structural damage inside the knee.
Persistent Discomfort After Activity:
- You might notice that after physical activity, whether it’s walking, running, or standing for extended periods, your knee feels sore or uncomfortable. This post-activity discomfort could signal early signs of overuse or degeneration within the knee joint, potentially leading to conditions like patellar tendonitis or cartilage wear.
Recognizing these early signs of knee pain can help you seek treatment before the condition worsens. While some discomfort might be manageable with rest and minor adjustments, persistent or worsening symptoms warrant professional evaluation. Early intervention can prevent long-term damage and improve outcomes for knee health.
Proven Treatments: Effective Solutions to Manage Knee Pain
Once you identify the signs of knee pain, you may want to explore treatments to address the issue and prevent it from worsening. For minor pain or inflammation, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (the RICE method) could provide immediate relief. You might consider over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen to reduce pain and swelling. If these approaches offer temporary relief, it may be a sign that your knee pain can be managed without more invasive treatments.
However, if the pain persists or worsens, physical therapy could be a crucial next step. A physical therapist might help you strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving stability and reducing strain on the joint. In some cases, exercises to improve flexibility and balance may also reduce pressure on the knee.
If your knee pain stems from conditions like osteoarthritis or significant injury, you may need to explore more advanced options. Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief for several months, though these treatments should be used cautiously and under a doctor’s supervision. If conservative treatments don’t work, surgery, such as knee arthroscopy or partial knee replacement, might become necessary.
How to Prevent Knee Pain from Returning
While treatments can offer short-term relief, you might want to focus on long-term strategies to keep knee pain at bay. Regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, could help maintain joint flexibility without placing excessive strain on your knees. You may also want to maintain a healthy weight, as carrying extra weight could increase stress on the knees, exacerbating pain and worsening existing conditions.
In addition to strengthening exercises, stretching the muscles surrounding your knee could also play a role in preventing future pain. If you find that your knee issues are related to overuse or improper movement patterns, wearing knee braces or using orthotics in your shoes might provide additional support and prevent further injury.
Taking Action to Manage Knee Pain for the Long Term
Knee pain can be debilitating, but if you recognize the early signs and take action, you may avoid more serious complications down the line. By exploring proven treatments and adopting long-lasting strategies, you could find effective relief and improve your quality of life.